Arnold Chiari Malformation
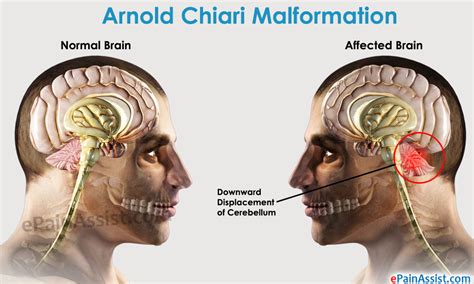
Arnold Chiari Malformation, or Chiari Malformation (CM) as it is commonly known, is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects the brain's structure and function. Named after the Austrian pathologist Hans Chiari, who first described the condition in the late 19th century, it has since become a topic of interest and research in the medical community.
Chiari Malformation is a neurological disorder characterized by the displacement of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum, the opening at the base of the skull. This displacement can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, making it a challenging condition to diagnose and treat.
In this in-depth exploration, we will delve into the world of Chiari Malformation, uncovering its types, causes, symptoms, and the latest advancements in diagnosis and treatment. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this intriguing and impactful condition.
Understanding the Complexity of Chiari Malformation

Chiari Malformation is not a single disorder but a spectrum of related conditions, each with its unique characteristics and severity. The malformation can be classified into several types, each presenting a different set of challenges.
Types of Chiari Malformation
There are primarily four types of Chiari Malformation, each identified by the extent of cerebellar tissue descent into the foramen magnum:
- Type I Chiari Malformation: This is the most common type, often referred to as CM I. It is characterized by the herniation of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum without involving the brainstem. CM I can be further classified into mild, moderate, and severe based on the extent of herniation.
- Type II Chiari Malformation: Also known as CM II or Arnold-Chiari Malformation, this type involves the herniation of both the cerebellar tonsils and a portion of the brainstem. CM II is often associated with myelomeningocele, a type of spina bifida.
- Type III Chiari Malformation: A rare and severe form, CM III involves the herniation of the cerebellum and brainstem through the foramen magnum, often into the spinal cord. This type can lead to life-threatening complications and requires immediate medical attention.
- Type IV Chiari Malformation: CM IV is the most severe and least common type. It is characterized by an incomplete or underdeveloped cerebellum, with portions of the brainstem and spinal cord exposed. CM IV often leads to significant neurological deficits and can be fatal.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of Chiari Malformation are not fully understood, but researchers believe it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Here are some key points regarding the causes and risk factors:
- Genetics: Some studies suggest a genetic component, with Chiari Malformation running in families. Certain genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities have been linked to the condition.
- Congenital Factors: Chiari Malformation can be present at birth (congenital), often due to improper development of the brain and spinal cord during fetal development.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medications during pregnancy may increase the risk of Chiari Malformation.
- Spinal Cord Trauma: In some cases, trauma to the spinal cord or brain can lead to the development of Chiari Malformation.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

The symptoms of Chiari Malformation can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some individuals may experience no symptoms at all, while others may have a range of neurological and physical issues.
Common Symptoms
- Headaches: Severe headaches, often triggered by coughing, sneezing, or straining, are a hallmark symptom of Chiari Malformation. These headaches can be debilitating and are often the first indicator of the condition.
- Neck Pain: Many individuals with Chiari Malformation experience chronic neck pain, which can radiate to the shoulders and back.
- Balance and Coordination Issues: Difficulty with balance, coordination, and gait can be present, making everyday activities challenging.
- Numbness and Tingling: Patients may experience numbness, tingling, or a “pins and needles” sensation in the hands, arms, or legs.
- Vision and Hearing Problems: Chiari Malformation can affect vision, leading to blurred or double vision. Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus) may also occur.
- Sleep Disorders: Insomnia, sleep apnea, and other sleep-related issues are common among those with Chiari Malformation.
- Dizziness and Vertigo: Dizziness and a sense of spinning (vertigo) can be disruptive and impact daily life.
Diagnosis and Medical Tests
Diagnosing Chiari Malformation involves a comprehensive approach, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and advanced imaging techniques. Here’s an overview of the diagnostic process:
- Medical History and Examination: Healthcare providers will ask about symptoms, medical history, and any family history of neurological disorders. A physical examination will assess muscle strength, reflexes, and coordination.
- Neuroimaging: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the gold standard for diagnosing Chiari Malformation. MRI scans provide detailed images of the brain and spinal cord, allowing doctors to visualize the cerebellar tonsils and their position.
- Other Tests: Depending on the symptoms and suspected complications, additional tests may be ordered, such as cerebrospinal fluid analysis, electromyography (EMG), or evoked potential studies.
Treatment Options and Management
The treatment approach for Chiari Malformation depends on the type, severity, and symptoms experienced by the individual. Here’s an overview of the various treatment strategies:
Conservative Management
For individuals with mild symptoms or no symptoms at all, conservative management may be recommended. This approach focuses on symptom relief and includes the following strategies:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage headaches and neck pain.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises and physical therapy can improve strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as heavy lifting or high-impact sports, can be beneficial.
- Pain Management: For severe pain, prescription medications or nerve blocks may be considered.
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is often the preferred treatment for individuals with severe symptoms or complications. The goal of surgery is to relieve pressure on the brain and spinal cord, allowing the cerebrospinal fluid to flow properly. The most common surgical procedure for Chiari Malformation is:
- Decompressive Craniectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the skull bone to create more space for the brain and cerebellar tonsils. It can significantly improve symptoms and prevent further complications.
Post-Surgical Care and Rehabilitation
Following surgery, patients typically require a period of recovery and rehabilitation. This may include:
- Rest and gradual return to normal activities.
- Physical therapy to regain strength and mobility.
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress and manage any post-surgical issues.
Living with Chiari Malformation
Managing Chiari Malformation is a lifelong journey, and individuals with the condition often need ongoing support and care. Here are some key aspects of living with Chiari Malformation:
Support and Community
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with Chiari Malformation can be immensely helpful. Support groups, both online and in-person, provide a platform for sharing experiences, coping strategies, and emotional support.
Long-Term Management
Regular medical check-ups and monitoring are essential to manage the condition effectively. This includes staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in treatment and being proactive in symptom management.
Coping Strategies
Developing effective coping strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with Chiari Malformation. This may include stress management techniques, relaxation exercises, and finding hobbies or activities that bring joy and distraction from symptoms.
Nutrition and Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help manage symptoms and promote overall well-being. Certain dietary changes, such as avoiding foods that trigger headaches or inflammation, may also be beneficial.
Future Perspectives and Research

The field of Chiari Malformation research is evolving, and new insights are continuously emerging. Here are some key areas of focus for future advancements:
Genetic Research
Understanding the genetic basis of Chiari Malformation is a crucial area of research. By identifying specific genetic mutations and biomarkers, researchers hope to develop targeted therapies and improve diagnostic accuracy.
Neurological Complications
Chiari Malformation can lead to various neurological complications, including hydrocephalus, syringomyelia, and spinal cord dysfunction. Ongoing research aims to better understand these complications and develop more effective treatment strategies.
Non-Surgical Interventions
While surgery is a common treatment option, researchers are exploring alternative, non-surgical interventions. These may include novel medications, physical therapy protocols, and innovative technologies to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Patient-Reported Outcomes
Patient-reported outcomes and quality-of-life assessments are gaining importance in Chiari Malformation research. By understanding the impact of the condition on daily life, researchers can develop more patient-centric treatment approaches.
| Chiari Malformation Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Type I | Most common, herniation of cerebellar tonsils without brainstem involvement. |
| Type II | Herniation of cerebellar tonsils and brainstem, often associated with myelomeningocele. |
| Type III | Severe, herniation of cerebellum and brainstem into the spinal cord, requiring immediate medical attention. |
| Type IV | Least common, incomplete or underdeveloped cerebellum with exposed brainstem and spinal cord. |

Can Chiari Malformation be cured completely?
+
While there is no cure for Chiari Malformation, surgical intervention can significantly improve symptoms and prevent further complications. However, some individuals may still experience residual symptoms post-surgery, requiring ongoing management.
What are the long-term complications of Chiari Malformation?
+
Long-term complications can include chronic pain, neurological deficits, and the development of other conditions like hydrocephalus or syringomyelia. Regular medical follow-up is essential to manage these complications effectively.
How does Chiari Malformation affect daily life?
+
The impact on daily life varies depending on the type and severity of Chiari Malformation. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms that can be managed with conservative measures, while others may face significant challenges with activities of daily living due to pain, balance issues, and fatigue.
Is Chiari Malformation a progressive condition?
+
Chiari Malformation can progress over time, particularly if left untreated. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help slow down or halt the progression of the condition, improving long-term outcomes.
What are the chances of a successful recovery after surgery for Chiari Malformation?
+
Surgical outcomes for Chiari Malformation are generally positive, with many individuals experiencing significant symptom relief. However, recovery times can vary, and some patients may require additional interventions or ongoing symptom management.



