Average Male Refractory Period
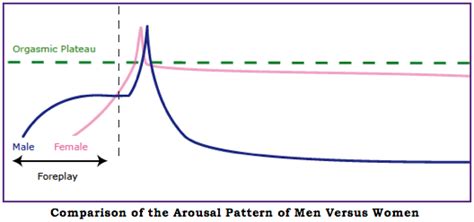
The male refractory period is a fascinating aspect of human sexuality, and understanding its intricacies can provide valuable insights into the complex world of sexual health and performance. This article aims to delve into the average male refractory period, exploring its definition, duration, and the factors that influence it.
Understanding the Male Refractory Period
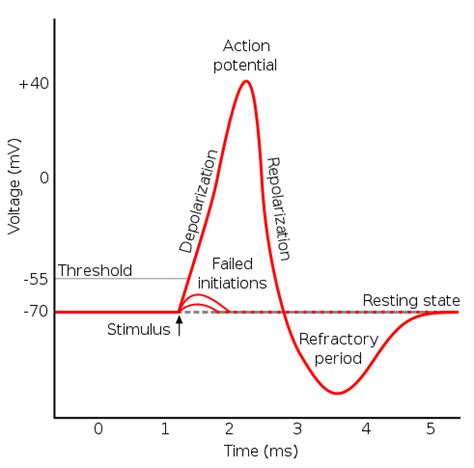
The refractory period, in the context of male sexual function, refers to the time span after ejaculation during which a man is unable to achieve another erection and subsequently engage in sexual intercourse. It is a natural physiological process that occurs as the body recovers and prepares for potential subsequent sexual encounters.
While the refractory period is a normal and expected phenomenon, its duration and intensity can vary significantly among individuals. This variability is influenced by a multitude of factors, including age, overall health, hormonal balance, and even psychological factors such as stress and emotional well-being.
Duration of the Average Male Refractory Period
Determining the average duration of the male refractory period is a complex task, as it involves considering the diverse range of physiological and psychological factors that contribute to sexual function. Research suggests that the refractory period can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, with the average duration falling within the range of 10 to 30 minutes for most men.
It is important to note that this average is just a general guideline and does not account for individual variations. Some men may experience a much shorter refractory period, allowing for rapid successive sexual encounters, while others may require a longer recovery time.
Factors Influencing the Refractory Period
Several key factors can influence the duration and intensity of the male refractory period:
- Age: As men age, the refractory period tends to increase in duration. This is often attributed to natural hormonal changes and the general decline in overall sexual function that can occur with advancing age.
- Hormonal Balance: Hormones play a crucial role in sexual function. Testosterone, in particular, is associated with libido and sexual performance. Men with optimal testosterone levels may experience a shorter refractory period.
- Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular issues, can impact sexual function and potentially lengthen the refractory period. Additionally, medications used to manage these conditions may also influence sexual response.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and emotional well-being can significantly affect the refractory period. Men who experience high levels of stress or have underlying psychological issues may find that their refractory period is prolonged.
- Sexual Technique and Stimulation: The intensity and duration of sexual stimulation can influence the refractory period. Prolonged or intense stimulation may lead to a longer recovery time, while more moderate stimulation could result in a shorter refractory period.
Performance Analysis and Comparison
Comparing the refractory period across different age groups and demographics provides valuable insights into the variations in male sexual function. Research has shown that younger men, typically in their late teens and early twenties, often experience a shorter refractory period, allowing for more frequent and rapid sexual encounters.
As men progress into their thirties and beyond, the refractory period tends to lengthen. This natural progression is attributed to the hormonal changes that occur with aging, such as a gradual decline in testosterone levels. However, it is important to note that individual variations can still be significant, and some older men may experience shorter refractory periods than the average.
| Age Group | Average Refractory Period |
|---|---|
| Teens and Early 20s | 5-15 minutes |
| Mid-20s to 30s | 10-20 minutes |
| 40s and Beyond | 20-30 minutes |
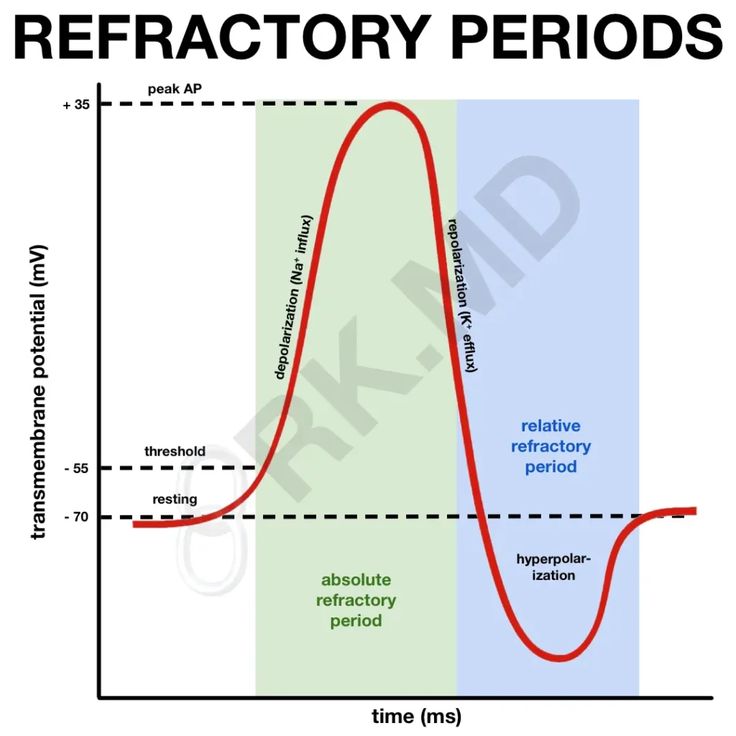
Implications and Future Considerations
Understanding the average male refractory period and the factors that influence it can have significant implications for sexual health and relationship dynamics. For men experiencing concerns about their refractory period, whether it is too short or too long, there are strategies and treatments available to optimize sexual function.
For instance, men with a shorter-than-average refractory period may benefit from techniques that promote sustained arousal and control ejaculatory response. On the other hand, those with a prolonged refractory period can explore options such as lifestyle modifications, stress management, and, in some cases, medical interventions to address underlying health issues.
As research in the field of sexual medicine continues to advance, we can expect to gain a deeper understanding of the male refractory period and develop more effective strategies for managing it. This knowledge will not only benefit individual men but also contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of human sexuality and its complex interplay with physical and psychological health.
Can the refractory period be reduced through training or practice?
+While the refractory period is primarily influenced by physiological factors, some men may be able to reduce its duration through specific techniques and practices. These techniques often focus on controlling ejaculatory response and prolonging arousal. However, it is important to approach these methods with caution and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and appropriate for individual needs.
Are there any medical conditions that can affect the refractory period?
+Yes, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular issues, and hormonal imbalances, can impact the refractory period. Additionally, medications used to manage these conditions may also affect sexual function. It is crucial for men experiencing concerns about their refractory period to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if an underlying medical condition is a contributing factor.
Can stress and anxiety affect the refractory period?
+Absolutely. Stress and anxiety are known to have a significant impact on sexual function, including the refractory period. Men experiencing high levels of stress or anxiety may find that their refractory period is prolonged. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and seeking support can help improve sexual function and reduce the impact of stress on the refractory period.



