Chronic Cerebral Infarction
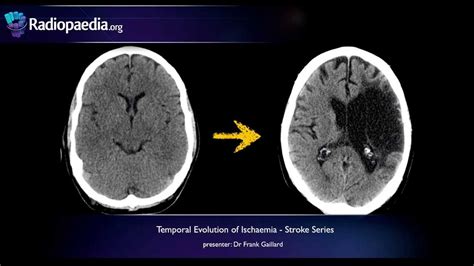
Chronic Cerebral Infarction (CCI), also known as chronic cerebral ischemia, is a neurological condition that develops over time and can lead to significant cognitive and functional impairments. It is a result of multiple small strokes or infarcts in the brain, often occurring in the cerebral arteries, and has a profound impact on an individual's quality of life.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of Chronic Cerebral Infarction, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and the various treatment approaches. By understanding this complex condition, we aim to shed light on the challenges faced by those affected and provide valuable insights for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike.
Understanding Chronic Cerebral Infarction: An Overview

Chronic Cerebral Infarction is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by recurrent ischemic events in the brain. These events, typically resulting from a blockage or narrowing of cerebral arteries, lead to reduced blood flow and subsequent damage to brain tissue. Over time, the cumulative effect of these infarcts can cause significant cognitive decline and functional impairments.
The condition is often associated with aging and is more prevalent in individuals with cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and atherosclerosis. However, CCI can also occur in younger individuals, particularly those with certain genetic predispositions or underlying medical conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors
CCI is primarily caused by the narrowing or blockage of cerebral arteries, which can result from various factors. Atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries, is a major contributor to CCI. These deposits, known as plaques, can restrict blood flow and lead to ischemic events.
Additionally, CCI can be triggered by conditions such as carotid artery stenosis, where the carotid arteries become narrowed, reducing blood flow to the brain. Other risk factors include hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Genetic predispositions and certain medical conditions, such as atrial fibrillation, can also increase the likelihood of developing CCI.
| Risk Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis | Buildup of fatty plaques in arteries |
| Carotid Artery Stenosis | Narrowing of carotid arteries |
| Hypertension | High blood pressure |
| Diabetes | Impaired blood sugar regulation |
| High Cholesterol | Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol |
| Smoking | Cigarette smoking |
| Obesity | Excess body weight |
| Sedentary Lifestyle | Lack of physical activity |
| Genetic Predisposition | Inherited genetic factors |

Symptoms and Diagnosis of Chronic Cerebral Infarction

The symptoms of Chronic Cerebral Infarction can vary widely depending on the location and severity of the infarcts. Common symptoms include cognitive impairments, such as memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and impaired judgment. Patients may also experience motor deficits, such as weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, known as hemiparesis or hemiplegia.
Cognitive Impairments
Cognitive impairments are a hallmark of CCI. Patients may struggle with short-term memory, have difficulty with problem-solving and decision-making, and experience a decline in their ability to perform daily activities independently. Language difficulties, such as aphasia, may also occur, affecting the ability to understand or express language.
Motor Deficits
Motor deficits are common in CCI and can range from mild weakness to complete paralysis. Hemiparesis, weakness on one side of the body, is a frequent occurrence. Patients may also experience balance and coordination problems, making walking and performing fine motor tasks challenging.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Chronic Cerebral Infarction involves a comprehensive evaluation by a neurologist or a specialist in vascular neurology. The diagnostic process typically includes a detailed medical history, a physical examination, and a series of neurological tests.
Neuroimaging, such as MRI or CT scans, plays a crucial role in diagnosing CCI. These imaging techniques can reveal areas of infarction and help identify the extent and severity of the damage. Additionally, blood tests may be performed to assess cardiovascular risk factors and rule out other potential causes of symptoms.
Treatment and Management of Chronic Cerebral Infarction
The treatment and management of Chronic Cerebral Infarction aim to improve symptoms, prevent further infarcts, and enhance the patient’s quality of life. While there is currently no cure for CCI, a multidisciplinary approach can help manage the condition and slow its progression.
Medications
Medications are a cornerstone of CCI treatment. Antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, are commonly prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clots and prevent further ischemic events. Statins may be used to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the progression of atherosclerosis.
In cases where blood pressure is a significant factor, antihypertensive medications are prescribed to control hypertension. Diabetes management is also crucial, and medications may be adjusted to optimize blood sugar control.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential for managing Chronic Cerebral Infarction. Smoking cessation is a critical step, as it reduces the risk of further vascular damage. A heart-healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help manage cardiovascular risk factors.
Regular exercise, tailored to the patient's abilities, can improve cardiovascular health, enhance cognitive function, and promote overall well-being. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a safe and effective exercise program.
Rehabilitation and Supportive Care
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in managing the functional impairments associated with CCI. Physical therapy can help improve mobility, balance, and coordination. Occupational therapy focuses on developing strategies to overcome daily living challenges and improve independence.
Speech therapy may be beneficial for patients experiencing language difficulties. Cognitive rehabilitation techniques, such as memory training and problem-solving exercises, can help improve cognitive function and enhance the patient's overall quality of life.
Preventive Measures
Preventing further infarcts is a key aspect of CCI management. Regular medical check-ups and monitoring of cardiovascular risk factors are essential. Patients should be educated on the importance of medication adherence and the potential side effects of their prescribed drugs.
A holistic approach to CCI management involves addressing psychological well-being. Depression and anxiety are common in patients with CCI, and support groups or counseling can provide valuable emotional support.
Living with Chronic Cerebral Infarction: Challenges and Coping Strategies
Living with Chronic Cerebral Infarction presents unique challenges for patients and their caregivers. The cognitive and functional impairments associated with CCI can significantly impact an individual’s daily life and independence.
Challenges of Daily Living
CCI can affect an individual’s ability to perform basic activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and cooking. Patients may require assistance or adaptations to their living environment to ensure safety and independence. Caregivers play a vital role in providing support and assistance, and it is important for them to seek resources and support to manage their own well-being.
Emotional and Social Impact
The cognitive and functional changes associated with CCI can lead to emotional challenges, including depression, anxiety, and frustration. Patients may struggle with feelings of loss and grief as they adjust to their new limitations. Social isolation is also a concern, as individuals may withdraw from social activities due to their impairments.
Coping Strategies
Coping with the challenges of Chronic Cerebral Infarction requires a multifaceted approach. Patients and caregivers can benefit from the following strategies:
- Education and Support Groups: Learning about CCI and connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide valuable support and resources.
- Cognitive Training and Rehabilitation: Engaging in cognitive training exercises and rehabilitation programs can help improve cognitive function and overall quality of life.
- Emotional Support: Seeking counseling or joining support groups can provide a safe space to express emotions and cope with the emotional impact of CCI.
- Social Engagement: Staying connected with friends and family and participating in social activities, even if adapted to the individual's abilities, can help combat social isolation.
Future Perspectives and Research in Chronic Cerebral Infarction

Research in Chronic Cerebral Infarction is focused on improving our understanding of the condition and developing innovative treatment approaches. Advances in neuroimaging and genetics are providing new insights into the pathophysiology of CCI and its underlying causes.
Emerging Treatment Options
Researchers are exploring new therapeutic strategies, including the use of stem cell therapy and gene therapy, to promote brain repair and regeneration. Clinical trials are underway to assess the effectiveness of these emerging treatments in improving cognitive function and slowing disease progression.
Lifestyle Interventions
Lifestyle interventions, such as dietary modifications and exercise programs tailored to the needs of CCI patients, are being studied for their potential to improve cognitive function and overall health. Research suggests that a combination of physical activity, cognitive training, and social engagement can have a positive impact on brain health and cognitive reserve.
Rehabilitation Technologies
Advances in technology are also contributing to the development of innovative rehabilitation tools. Virtual reality and robotics are being explored as potential rehabilitation aids, offering immersive and engaging environments for cognitive and motor training.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Preventive strategies and risk reduction are key areas of focus in CCI research. Studies are investigating the impact of lifestyle modifications, such as dietary interventions and exercise programs, on reducing the incidence and severity of CCI. Additionally, research is underway to identify genetic markers that may help predict an individual’s risk of developing CCI, enabling targeted preventive measures.
How does Chronic Cerebral Infarction affect the brain's functions and cognitive abilities?
+CCI leads to recurrent ischemic events in the brain, causing damage to brain tissue. This damage can result in cognitive impairments, such as memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and impaired judgment. Over time, CCI can significantly impact an individual's cognitive abilities and overall brain function.
What are the long-term consequences of Chronic Cerebral Infarction if left untreated or unmanaged?
+If left untreated or unmanaged, CCI can lead to progressive cognitive decline, increased risk of future strokes, and severe functional impairments. It can significantly impact an individual's independence and quality of life, making it crucial to seek proper diagnosis and management.
Are there any natural remedies or dietary supplements that can help manage Chronic Cerebral Infarction symptoms?
+While a healthy diet and lifestyle are important, there is currently no evidence to support the use of specific natural remedies or dietary supplements as a standalone treatment for CCI. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before considering any complementary therapies.
In conclusion, Chronic Cerebral Infarction is a complex neurological condition that requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can work together to improve the quality of life for those affected by CCI. As research continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in the diagnosis and treatment of this challenging condition.



