Dcis Lumpectomy
Breast cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease, and its treatment often involves a range of surgical options. Among these, lumpectomy, also known as breast-conserving surgery, has gained prominence as a viable alternative to more extensive procedures. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the world of lumpectomy, focusing specifically on its application in the treatment of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a non-invasive form of breast cancer.
Understanding Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
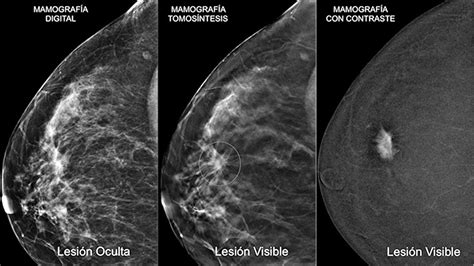
DCIS is a type of breast cancer that develops in the milk ducts and remains confined within the ductal system. Unlike invasive breast cancer, where cancer cells have broken through the duct walls and spread to nearby tissues, DCIS is non-invasive. However, this does not mean it should be taken lightly; DCIS is a precursor to invasive cancer, and its presence indicates a heightened risk of developing invasive disease in the future.
The standard treatment approach for DCIS often involves a combination of lumpectomy and radiation therapy. Lumpectomy, as the name suggests, involves the removal of the cancerous area and a small margin of healthy tissue surrounding it, thereby conserving the breast. This procedure is often chosen over mastectomy, which entails the complete removal of the breast, as it offers a more aesthetically pleasing and less invasive option.
The Lumpectomy Procedure for DCIS

Lumpectomy for DCIS is a delicate surgical procedure performed by a breast surgeon. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the process:
Pre-Surgical Planning
Before the lumpectomy, the patient will undergo a series of diagnostic tests, including mammograms, ultrasounds, and possibly a biopsy to confirm the presence of DCIS. The surgeon will carefully review these images and the biopsy results to plan the surgery.
During this stage, the surgeon will also discuss the potential risks and benefits of the procedure with the patient, ensuring they understand the implications and have the opportunity to ask questions.
Surgical Technique
On the day of the surgery, the patient is typically administered local anesthesia to numb the breast area. In some cases, a sedative may be given to help the patient relax.
- Incision: The surgeon makes a small incision, usually less than an inch long, near the area of the DCIS. The precise location and size of the incision depend on the size and location of the tumor.
- Tumor Removal: Using specialized surgical instruments, the surgeon carefully removes the cancerous tissue, along with a small margin of healthy tissue. This margin is crucial to ensure that all the cancerous cells are eliminated.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: In certain cases, especially if there is a concern about the potential spread of cancer, the surgeon may also perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy. This involves removing a few lymph nodes near the tumor to check for cancer cells.
- Closure: Once the tumor and any necessary lymph nodes have been removed, the surgeon closes the incision using stitches or surgical staples. The wound is then dressed and covered with a sterile bandage.
Post-Surgical Care
After the lumpectomy, patients typically stay in the recovery area for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications. Most patients can go home the same day, but some may require an overnight stay if there are concerns about pain management or other factors.
During the recovery period, which can last several weeks, patients are advised to take it easy and avoid strenuous activities. Pain medication may be prescribed to manage any discomfort. It is crucial to follow the surgeon's post-operative care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.
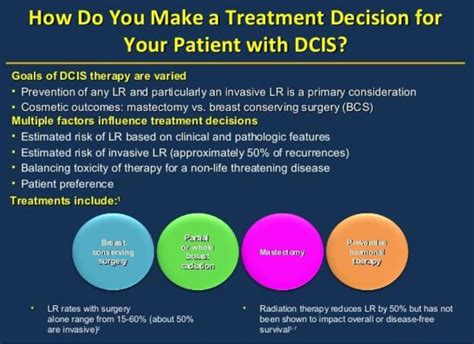
Lumpectomy vs. Mastectomy for DCIS
When faced with the diagnosis of DCIS, patients often have the option to choose between lumpectomy and mastectomy. Here’s a comparison of these two surgical approaches:
| Lumpectomy | Mastectomy |
|---|---|
| Conserves the breast | Removes the entire breast |
| Less invasive | More extensive procedure |
| Shorter recovery time | Longer recovery period |
| Typically combined with radiation therapy | May be followed by radiation or reconstructive surgery |
| Preserves breast aesthetics | Can affect body image and self-esteem |
| Lower risk of complications | Higher risk of complications |
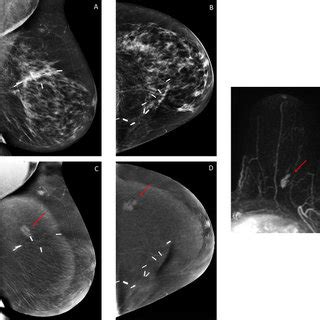
The choice between lumpectomy and mastectomy is highly personalized and depends on various factors, including the patient's overall health, the size and location of the tumor, and personal preferences. It is crucial to discuss these options thoroughly with a healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
The Role of Radiation Therapy
Following a lumpectomy for DCIS, radiation therapy is often recommended to ensure that any remaining cancer cells are eliminated. This additional treatment helps reduce the risk of the cancer returning.
Radiation Therapy Process
Radiation therapy for DCIS typically involves external beam radiation, where high-energy X-rays are directed at the breast from outside the body. Here’s a brief overview of the process:
- Planning: Before starting radiation therapy, the patient undergoes a planning session, often referred to as a simulation. This involves taking X-rays and CT scans to determine the exact treatment area.
- Treatment Sessions: Radiation therapy is usually delivered in daily sessions, five days a week, for several weeks. Each session lasts for a short duration, typically less than 30 minutes.
- Machine Calibration: The radiation machine is calibrated to deliver the precise dose of radiation to the treatment area while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues.
- Treatment Delivery: During each session, the patient lies on a treatment table while the radiation machine delivers the prescribed dose. The process is painless and typically takes only a few minutes.
After completing radiation therapy, patients typically have regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare team to monitor their recovery and ensure that the cancer has not returned.
Benefits and Considerations of Lumpectomy for DCIS

Lumpectomy offers several advantages for patients with DCIS. Firstly, it allows for the preservation of the breast, which is particularly important for those who value their body image and self-esteem. Additionally, lumpectomy is less invasive than mastectomy, resulting in a shorter recovery time and reduced risk of complications.
However, it's essential to note that lumpectomy is not without its challenges. The procedure may not be suitable for all patients, especially those with larger tumors or multiple areas of DCIS. In such cases, a mastectomy may be recommended to ensure complete removal of the cancerous tissue.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, lumpectomy carries certain risks and potential complications. These may include:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the incision site, which can be managed with antibiotics.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding is a rare but potential complication that may require additional treatment.
- Seroma Formation: A seroma is a collection of fluid at the surgical site. It usually resolves on its own but may require drainage in some cases.
- Pain and Discomfort: Patients may experience pain and tenderness in the breast area, which can be managed with pain medication.
- Lymphedema: In rare cases, especially if lymph nodes are removed, lymphedema (swelling in the arm) may occur. This condition requires ongoing management.
Conclusion
Lumpectomy is a valuable surgical option for patients with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), offering a less invasive approach to breast cancer treatment. When combined with radiation therapy, lumpectomy can effectively treat DCIS while preserving the breast. However, it’s crucial to carefully consider the individual circumstances and consult with a healthcare provider to make an informed decision about the most appropriate treatment plan.
As with any medical condition, staying informed and proactive is key. Patients should feel empowered to ask questions and seek second opinions to ensure they are receiving the best possible care.
How successful is lumpectomy in treating DCIS?
+Lumpectomy, when combined with radiation therapy, has a high success rate in treating DCIS. Studies show that the combination of these treatments can effectively eliminate the cancer and reduce the risk of recurrence. However, the success rate can vary based on individual factors such as the size and location of the tumor.
What are the long-term outcomes for patients who undergo lumpectomy for DCIS?
+Long-term outcomes for patients who undergo lumpectomy for DCIS are generally positive. Most patients experience a full recovery and lead normal, healthy lives. However, it’s important to note that DCIS increases the risk of developing invasive breast cancer in the future. Therefore, regular follow-up care and monitoring are essential to detect any potential recurrence early on.
Are there any alternatives to lumpectomy for treating DCIS?
+While lumpectomy is a common and effective treatment for DCIS, there are alternative options available. These include mastectomy, which removes the entire breast, and less invasive treatments such as cryotherapy or hormonal therapy. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the size and location of the tumor, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. It’s important to discuss these options thoroughly with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable approach.