How Big Is The Gaza Strip In Miles

The Gaza Strip, a narrow coastal territory located in the Middle East, has a unique and complex geopolitical status. This region, which is home to a significant Palestinian population, has been the center of global attention due to its historical, political, and humanitarian significance. As an expert in Middle Eastern affairs, I aim to provide a comprehensive analysis of the Gaza Strip, delving into its history, demographics, geopolitical challenges, and its implications for the broader region.
The Geography and Size of the Gaza Strip

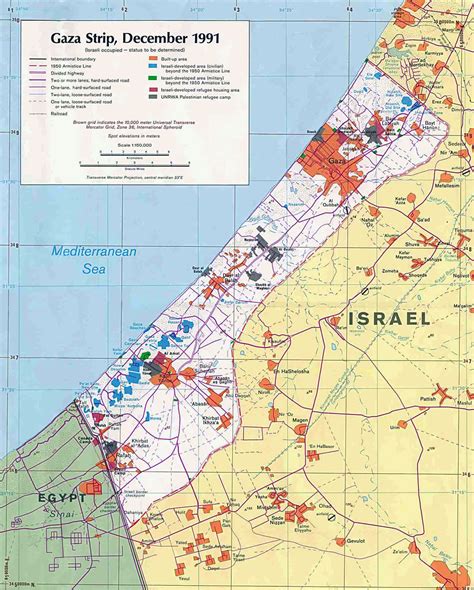
The Gaza Strip is a small, densely populated territory situated along the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It is a narrow landmass, approximately 25 miles (40 kilometers) long and varying in width between 4 and 9 miles (6 to 14 kilometers). With a total area of around 140 square miles (360 square kilometers), it is one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
Despite its small size, the Gaza Strip has a diverse landscape. The northern part of the territory features fertile agricultural land, with citrus groves and vegetable farms dotting the landscape. Moving southward, the terrain becomes more arid, characterized by sandy dunes and rocky outcrops. The coastline, with its beautiful beaches and azure waters, is a stark contrast to the inland desert-like conditions.
A Historical Perspective

The history of the Gaza Strip is intricate and deeply intertwined with the broader narrative of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Before the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, the Gaza Strip was part of the British Mandate of Palestine. The 1948 Arab-Israeli War led to the displacement of thousands of Palestinians, and the Gaza Strip came under the control of Egypt.
In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Israel captured the Gaza Strip from Egypt. This marked a significant turning point, as Israel's occupation of the territory brought about profound social, economic, and political changes for the Palestinian population.
The Oslo Accords of the 1990s established the Palestinian Authority, which was granted limited self-rule over parts of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. However, the situation in Gaza remained complex, with Israel retaining control over key aspects such as borders, airspace, and coastal waters.
Demographics and the Human Impact
The Gaza Strip is home to approximately 2.1 million people, with a predominantly young population. The high birth rate and limited economic opportunities have contributed to a rapidly growing population, which has put immense strain on the territory’s already limited resources.
The living conditions in Gaza are challenging, to say the least. The territory suffers from chronic unemployment, with rates exceeding 40% in some areas. Access to basic services such as healthcare and education is often inadequate, and the blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt has severely restricted the movement of goods and people, further exacerbating the humanitarian crisis.
| Population | Density (per sq. km) |
|---|---|
| 2.1 million | 5,000-8,000 (varies by region) |

The impact of the conflict and the blockade has been devastating for the people of Gaza. The lack of access to clean water, adequate healthcare, and sufficient food has led to a health crisis, with rising rates of malnutrition and disease. The educational system, already strained, faces challenges in providing quality education to the youth.
Geopolitical Challenges and International Relations
The Gaza Strip’s geopolitical position is highly sensitive and has significant implications for the region as a whole. The ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, coupled with the Israeli blockade, has led to a complex web of political and security issues.
The Israeli government cites security concerns as the primary reason for the blockade, arguing that it is necessary to prevent the smuggling of weapons and maintain stability. However, this policy has been widely criticized by human rights organizations and the international community, as it disproportionately affects the civilian population and hinders Gaza's economic development.
The situation in Gaza has also been a source of tension between Israel and Egypt. The Rafah border crossing, which connects Gaza to Egypt, is often a point of contention, with both countries asserting control and imposing restrictions.
International Efforts and Peace Initiatives
The international community has recognized the dire situation in Gaza and has made various efforts to alleviate the humanitarian crisis. Numerous aid organizations and NGOs operate in the territory, providing essential services and supporting local initiatives.
Political efforts to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict have been ongoing for decades, with various peace initiatives and proposals put forward. The two-state solution, which envisions an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, remains the most widely supported framework. However, reaching a sustainable and mutually agreed-upon solution has proven to be an immense challenge.
The Gaza Strip, with its unique geopolitical position and complex history, serves as a microcosm of the broader Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Understanding the intricacies of this territory is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the dynamics of the region and the ongoing efforts towards peace and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the population density of the Gaza Strip compared to other regions?
+The population density of the Gaza Strip varies, ranging from 5,000 to 8,000 people per square kilometer. This makes it one of the most densely populated areas in the world, with some regions exceeding the density of even the most populous cities.
How has the blockade affected the economy of the Gaza Strip?
+The blockade has had a devastating impact on the economy of the Gaza Strip. It has restricted the import and export of goods, limited access to markets, and hindered economic growth. The result is a high unemployment rate and a struggling private sector.
What are the key challenges faced by the healthcare system in Gaza?
+The healthcare system in Gaza faces numerous challenges, including a shortage of medical supplies, limited access to specialized care, and a lack of infrastructure and equipment. The blockade has exacerbated these issues, making it difficult to provide adequate healthcare to the population.



