Humidity Explained

Humidity is a fundamental atmospheric concept that plays a pivotal role in our daily lives and has far-reaching implications across various industries. From the comfort of our homes to the efficiency of industrial processes, understanding humidity is essential. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of humidity, exploring its nature, measurement, and impact on different aspects of our world.
Unveiling the Nature of Humidity

At its core, humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. This seemingly simple definition belies the complex dynamics and interactions that humidity entails. Water vapor is an integral part of the Earth’s natural water cycle, continuously evaporating from water bodies, transpiring from plants, and condensing to form clouds and precipitation.
Humidity is a dynamic variable, influenced by a myriad of factors such as temperature, air pressure, and the presence of moisture sources. It is this variability that makes humidity an intriguing and challenging phenomenon to study and control.
To comprehend humidity, we must explore the different forms it takes and the ways it manifests in our environment. Relative humidity, specific humidity, and absolute humidity are the three primary measures used to quantify humidity levels.
Relative Humidity: A Common Measure
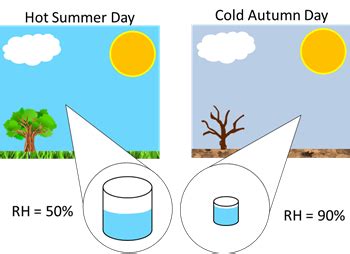
Relative humidity (RH) is the most commonly cited measure of humidity. It represents the amount of moisture in the air relative to the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at a given temperature. RH is expressed as a percentage, with 100% indicating saturation and the potential for condensation.
For instance, if the air at a certain temperature has 50% RH, it means it contains half the moisture it can possibly hold. This measure is particularly useful for understanding human comfort levels and the potential for moisture-related issues in various applications.
| Relative Humidity Range | Comfort Level |
|---|---|
| 30% - 50% | Optimal for human comfort |
| 50% - 70% | Mild discomfort, potential for mold and mildew |
| 70% - 100% | High discomfort, condensation likely |

Specific and Absolute Humidity: Technical Measures
While relative humidity is widely used, specific humidity and absolute humidity provide more technical insights. Specific humidity measures the mass of water vapor per unit mass of dry air, typically expressed in grams per kilogram (g/kg). Absolute humidity, on the other hand, refers to the actual mass of water vapor present in a given volume of air, measured in grams per cubic meter (g/m³).
These measures are crucial in industries such as meteorology, agriculture, and industrial processes, where precise control and understanding of humidity levels are essential.
Measuring Humidity: Tools and Techniques
The measurement of humidity is a critical aspect of its study and control. A range of tools and techniques are employed to gauge humidity levels accurately.
Psychrometers and Hygrometers
Psychrometers, also known as wet-and-dry bulb thermometers, are traditional instruments used to measure humidity. They consist of two thermometers, one with a wet wick and one dry. The evaporation of moisture from the wet bulb lowers the temperature, allowing for the calculation of humidity based on the difference between the two readings.
Hygrometers are modern electronic devices that measure humidity using various sensors. Capacitive hygrometers, for instance, utilize the principle of capacitance change in response to humidity variations. These devices offer precise and real-time humidity measurements, making them invaluable in various applications.
Humidity Sensors and Data Loggers
In industrial and research settings, humidity sensors are integrated into sophisticated systems to monitor and control humidity levels. These sensors can be calibrated to provide highly accurate readings, ensuring precise environmental control.
Data loggers are often employed to record humidity levels over extended periods, providing valuable insights into humidity trends and patterns. These devices are particularly useful in agriculture, where understanding humidity dynamics is crucial for crop growth and pest control.
The Impact of Humidity: Comfort, Health, and Industry
Humidity’s influence extends far beyond the atmosphere, impacting our daily lives and various industries in profound ways.
Human Comfort and Health
Humidity plays a pivotal role in human comfort and well-being. High humidity levels can lead to discomfort, fatigue, and even health issues such as respiratory problems and skin irritation. Conversely, low humidity can cause dry skin, eye irritation, and respiratory discomfort.
Maintaining optimal humidity levels is crucial for indoor environments, especially in homes, offices, and healthcare facilities. This is achieved through the use of dehumidifiers and humidifiers, which regulate humidity to promote comfort and health.
Industrial and Agricultural Applications
In industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, humidity control is essential for product quality and safety. Excessive humidity can lead to corrosion, mold growth, and product degradation, while low humidity can cause drying and cracking of materials.
In agriculture, humidity management is critical for crop growth and protection. Excessive humidity can promote the growth of pests and diseases, while controlled humidity levels can enhance crop yield and quality. Greenhouses, for instance, employ humidity control systems to create optimal growing conditions for various plants.
Environmental Impact and Climate Studies
Humidity is a key factor in understanding and predicting weather patterns and climate change. It influences the formation of clouds, precipitation, and extreme weather events. Long-term humidity trends can provide valuable insights into climate dynamics and the potential impacts of global warming.
Climate scientists and meteorologists use humidity data alongside other atmospheric variables to model and forecast weather patterns, helping communities prepare for and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Future Implications and Innovations
As our understanding of humidity deepens, so do the opportunities for innovation and technological advancements.
Smart Humidity Control Systems
The integration of humidity sensors with smart home and building automation systems is a burgeoning area of innovation. These systems can automatically adjust humidity levels based on occupant preferences and environmental conditions, optimizing comfort and energy efficiency.
In commercial and industrial settings, smart humidity control systems can enhance productivity and product quality by maintaining precise humidity levels in critical areas.
Advanced Humidity Monitoring in Agriculture
The future of agriculture lies in precision farming, where advanced sensors and data analytics are used to optimize crop growth and resource management. Humidity sensors, integrated with soil moisture sensors and weather data, can provide real-time insights into crop water requirements, helping farmers make informed decisions about irrigation and crop protection.
Humidity in Space Exploration
As humanity ventures into space exploration, humidity control becomes a critical aspect of sustainable habitation. Controlling humidity levels in spacecraft and habitats is essential for crew health and comfort, as well as for the functionality of electronic equipment.
Advanced humidity control systems, coupled with efficient water recycling technologies, are being developed to support long-duration space missions and the potential colonization of other celestial bodies.
What are the health implications of high humidity?
+High humidity can lead to a range of health issues, including respiratory problems, skin irritation, and fatigue. It can also promote the growth of mold and mildew, which can trigger allergies and respiratory conditions.
How does humidity affect electronic devices?
+Excessive humidity can cause condensation on electronic components, leading to short circuits and corrosion. Low humidity, on the other hand, can cause static electricity buildup, potentially damaging sensitive electronics.
What are the challenges in measuring humidity accurately?
+Measuring humidity accurately can be challenging due to factors like temperature fluctuations, air pressure changes, and the presence of contaminants. Advanced humidity sensors and calibration techniques are employed to ensure precise measurements.