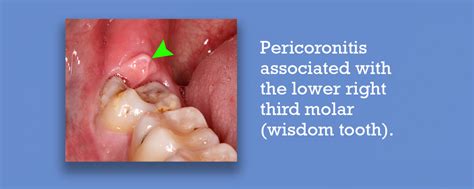
'Pericoronitis

Pericoronitis is a dental condition that affects many individuals, often causing significant discomfort and pain. It occurs when the soft tissue surrounding a partially erupted or impacted tooth becomes inflamed and infected. This condition is most commonly associated with the wisdom teeth, or third molars, but can also affect other teeth in certain circumstances.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of pericoronitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options. By understanding this dental issue, individuals can better recognize the signs and seek appropriate care, ensuring a healthier oral cavity.
Understanding Pericoronitis: A Comprehensive Overview

Pericoronitis is an inflammatory condition that develops when the gum tissue, or operculum, surrounding a partially erupted tooth becomes infected. This often occurs due to the accumulation of bacteria and food debris in the space between the tooth and the gum, leading to a localized infection.
The condition is more frequently seen in young adults, particularly during the late teens and early twenties, when the wisdom teeth typically erupt. However, pericoronitis can affect individuals of any age, especially if they have a partially erupted or impacted tooth.
Causes of Pericoronitis
The primary cause of pericoronitis is the presence of a partially erupted tooth, which creates a pocket or space between the tooth and the gum. This area can trap food particles and bacteria, leading to an infection. The following factors can contribute to the development of pericoronitis:
- Impacted Wisdom Teeth: Wisdom teeth that are unable to fully erupt due to lack of space or improper alignment are a common cause of pericoronitis. The soft tissue covering the partially erupted tooth can become irritated and infected.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene practices can increase the risk of pericoronitis. When teeth are not properly cleaned, bacteria can accumulate, leading to infection.
- Trauma or Injury: Trauma to the mouth, such as a blow to the jaw or an injury during sports, can damage the soft tissue and increase the likelihood of pericoronitis.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing pericoronitis. This could be related to the position and alignment of their teeth, making certain individuals more susceptible.
Symptoms of Pericoronitis
The symptoms of pericoronitis can vary in severity and may include:
- Pain and Swelling: The most common symptom is pain and swelling around the affected tooth. The pain can be intense and may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck.
- Redness and Inflammation: The gum tissue surrounding the tooth may appear red, swollen, and inflamed.
- Bad Breath: The infection can cause an unpleasant odor and taste in the mouth.
- Difficulty Opening Mouth: In severe cases, pericoronitis can lead to difficulty opening the mouth fully.
- Fever and Lymph Node Swelling: In more advanced cases, pericoronitis can cause fever and swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of pericoronitis is typically based on a thorough examination of the mouth and the patient’s symptoms. The dentist will assess the affected area, checking for signs of inflammation and infection. In some cases, dental X-rays may be taken to evaluate the position and alignment of the tooth.
Treatment options for pericoronitis depend on the severity of the condition and may include:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene practices is crucial. The dentist may recommend gentle brushing and flossing techniques to prevent further infection.
- Antibiotics: In cases of severe infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the bacteria causing pericoronitis.
- Surgical Intervention: If pericoronitis recurs frequently or causes severe symptoms, surgical removal of the affected tooth (extraction) may be recommended.
Preventing Pericoronitis
Preventing pericoronitis primarily involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices. Here are some tips to reduce the risk:
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine, brushing twice a day and flossing daily. This helps remove plaque and bacteria, reducing the chances of infection.
- Use Mouthwash: Rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash can help kill bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoid Trauma: Take precautions to prevent oral injuries, especially if you have partially erupted teeth. Wear a mouthguard during sports activities to protect your teeth.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. They can monitor the development of your wisdom teeth and provide guidance on maintaining oral health.
Advanced Treatment Options for Pericoronitis
In some cases, pericoronitis may require more advanced treatment approaches. These options may be considered when the condition is severe or recurrent.
Pericoronal Flap Surgery
Pericoronal flap surgery is a surgical procedure that involves creating a flap of gum tissue to expose the partially erupted tooth. This allows for better access to clean and disinfect the area, reducing the risk of infection. The procedure is often performed under local anesthesia and may require a short recovery period.
Orthodontic Treatment
If pericoronitis is caused by misaligned or crowded teeth, orthodontic treatment may be recommended. Orthodontic appliances, such as braces or aligners, can help correct the alignment of the teeth, reducing the likelihood of pericoronitis. This approach is particularly beneficial for individuals with impacted wisdom teeth that are causing recurrent infections.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a relatively new treatment option for pericoronitis. The use of laser technology can help reduce inflammation, promote healing, and eliminate bacteria in the affected area. Laser therapy is often used as a complementary treatment alongside traditional methods.
Home Remedies
While professional treatment is essential for pericoronitis, there are some home remedies that can provide temporary relief and support the healing process. These include:
- Saltwater Rinses: Rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater can help reduce inflammation and draw out infection. Mix 1 teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth gently.
- Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help reduce swelling and provide pain relief. Wrap a few ice cubes in a thin towel and apply it to the outer cheek.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbal remedies, such as chamomile or sage, have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. You can make herbal teas and use them as mouth rinses to soothe the affected area.
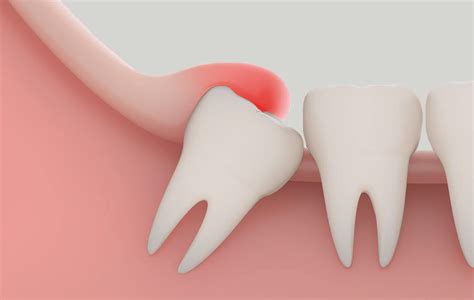
The Role of Wisdom Teeth in Pericoronitis
Wisdom teeth, or third molars, are often the primary culprits when it comes to pericoronitis. These teeth typically emerge during the late teens or early twenties, and their eruption can be challenging due to limited space in the jaw.
When wisdom teeth are impacted or partially erupted, they can create a pocket where food particles and bacteria can accumulate. This environment is ideal for the development of pericoronitis. The soft tissue surrounding the tooth can become inflamed and infected, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the condition.
Managing Wisdom Teeth to Prevent Pericoronitis
To prevent pericoronitis associated with wisdom teeth, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly. Here are some specific tips for managing wisdom teeth:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Your dentist can monitor the development and position of your wisdom teeth. They may recommend X-rays to assess the alignment and potential impact on surrounding teeth.
- Early Intervention: If your dentist identifies potential issues with your wisdom teeth, they may recommend early removal to prevent pericoronitis and other complications.
- Oral Hygiene Focus: Pay extra attention to cleaning your wisdom teeth and the surrounding area. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss carefully to remove food particles and bacteria.
Complications of Pericoronitis
If left untreated, pericoronitis can lead to several complications, including:
- Abscess Formation: The infection can spread and form an abscess, a collection of pus, in the soft tissue surrounding the tooth.
- Cellulitis: In severe cases, the infection can spread to the surrounding soft tissues, causing cellulitis, which is a serious bacterial skin infection.
- Jaw Osteomyelitis: In rare cases, the infection can spread to the jawbone, leading to a serious condition called osteomyelitis.
- Spread of Infection: Pericoronitis can lead to systemic infections if the bacteria enter the bloodstream. This can cause fever, chills, and other flu-like symptoms.
Future Perspectives and Research
While pericoronitis is a well-recognized dental condition, ongoing research aims to improve our understanding and management of the condition. Here are some future perspectives and areas of focus:
- Genetic Factors: Further research into the genetic factors associated with pericoronitis may help identify individuals at higher risk and develop targeted preventive measures.
- Inflammatory Response: Studying the body's inflammatory response to pericoronitis could lead to the development of more effective anti-inflammatory treatments.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Utilizing advanced imaging technologies, such as cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), can provide more detailed information about the position and alignment of teeth, aiding in the early detection and management of pericoronitis.
Conclusion
Pericoronitis is a dental condition that requires prompt attention and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can take an active role in maintaining their oral health. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and early intervention for impacted or partially erupted teeth are key to preventing and managing pericoronitis effectively.
Remember, if you experience symptoms of pericoronitis, it is crucial to seek professional dental care to receive the necessary treatment and prevent potential complications.
Can pericoronitis go away on its own?
+While mild cases of pericoronitis may resolve on their own with good oral hygiene and pain management, it is important to seek professional dental care. Leaving the condition untreated can lead to more severe infections and complications.
How long does it take to recover from pericoronitis?
+The recovery time for pericoronitis varies depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment. With proper care, most individuals can expect to recover within a few days to a week. However, in severe cases or after surgical interventions, recovery may take longer.
Is pericoronitis contagious?
+Pericoronitis itself is not contagious. However, the bacteria associated with the condition can be transmitted through close contact or shared utensils. Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding sharing personal items can help prevent the spread of bacteria.



