What Are Hrt

Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), commonly referred to as hormone therapy (HT), is a medical treatment that involves the administration of hormones to individuals who have a deficiency or imbalance of these substances in their bodies. HRT is primarily used to alleviate symptoms associated with menopause in women and andropause in men, but it can also be employed to treat various other hormone-related conditions.
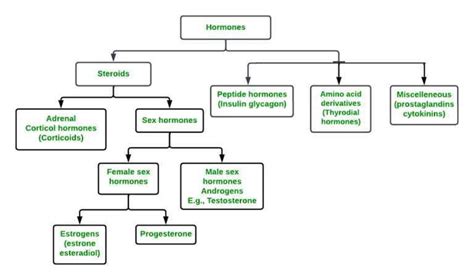
The primary purpose of HRT is to restore the balance of hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone in women and testosterone in men, which naturally decline with age. This therapy aims to improve the quality of life for individuals experiencing hormonal changes and reduce the risks associated with hormone deficiencies.
Understanding Hormone Replacement Therapy

Hormone replacement therapy is a specialized medical approach that involves the use of synthetic or natural hormones to mimic the body’s natural hormone production. It is often prescribed to individuals who are experiencing significant hormonal fluctuations or deficiencies, such as during menopause or andropause.
The most common form of HRT involves the use of estrogen, either alone or in combination with progesterone. Estrogen replacement therapy (ERT) is primarily used to alleviate menopausal symptoms in women, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood swings. In cases where a woman still has her uterus, progesterone is added to the regimen to reduce the risk of uterine cancer associated with long-term estrogen use.
For men experiencing andropause, or male menopause, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is often the chosen treatment. TRT aims to restore testosterone levels, which can decline with age, leading to symptoms such as reduced sex drive, fatigue, and muscle loss. It is important to note that TRT should be carefully monitored to avoid potential side effects and to ensure optimal hormone levels.
Types of Hormone Replacement Therapy
There are several methods of administering HRT, each with its own advantages and considerations:
- Oral Medication: HRT hormones can be taken in pill form, which is a convenient and widely used method. However, oral HRT can have a higher risk of side effects due to the hormones being processed through the liver.
- Skin Patches: Transdermal patches deliver hormones directly into the bloodstream through the skin. This method avoids first-pass metabolism in the liver, reducing the risk of certain side effects.
- Gel or Cream: Topical HRT applications, such as gels or creams, are another option. These are often used for individuals who cannot tolerate other forms of HRT.
- Vaginal Administration: For women experiencing vaginal symptoms, estrogen can be delivered directly to the vaginal tissue through a cream, ring, or tablet. This method provides localized relief without affecting other parts of the body.
- Injections: In some cases, HRT hormones can be administered via injection. This method provides a more controlled and consistent delivery of hormones but requires regular medical supervision.
The choice of HRT method depends on various factors, including the individual's medical history, personal preferences, and the specific hormone being administered.
| HRT Method | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Oral Medication | Convenient, widely available |
| Skin Patches | Avoid liver metabolism, easy to use |
| Gel or Cream | Suitable for sensitive individuals, localized effects |
| Vaginal Administration | Targeted relief for vaginal symptoms |
| Injections | Consistent hormone levels, long-lasting effects |
Potential Benefits of HRT
Hormone replacement therapy can provide numerous benefits, especially for individuals experiencing significant hormonal changes:
- Relief from Menopausal Symptoms: HRT is highly effective in reducing hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings, improving the overall quality of life during menopause.
- Bone Health: Estrogen plays a crucial role in bone health, and HRT can help prevent osteoporosis and reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women.
- Cardiovascular Protection: Some studies suggest that HRT may have cardiovascular benefits, particularly for women who start therapy early in menopause.
- Improved Sexual Function: Both estrogen and testosterone HRT can enhance sexual desire and function, addressing issues like vaginal dryness and erectile dysfunction.
- Mood and Cognitive Benefits: HRT may help improve mood and cognitive function, particularly in individuals with a history of depression or cognitive decline.
Considerations and Potential Risks
While HRT can be highly beneficial, it is essential to consider the potential risks and side effects, which may include:
- Increased Risk of Certain Cancers: Long-term use of HRT, particularly estrogen-only therapy, may slightly increase the risk of breast, ovarian, and uterine cancers.
- Blood Clots: HRT can increase the risk of blood clots, especially in individuals with a history of clotting disorders or who are inactive for extended periods.
- Cardiovascular Concerns: HRT may have varying effects on cardiovascular health, and its use in women with a history of heart disease requires careful consideration.
- Weight Gain: Some individuals may experience weight gain as a side effect of HRT, although this is not universally observed.
- Mood Changes: Hormone fluctuations can impact mood, and HRT may exacerbate existing mood disorders or cause new mood-related symptoms.
It is crucial to discuss the potential benefits and risks of HRT with a qualified healthcare professional to determine if this therapy is suitable for your specific needs and circumstances.
FAQ

What are the side effects of HRT?
+Side effects of HRT may include increased risk of certain cancers, blood clots, cardiovascular concerns, weight gain, and mood changes. However, the benefits and risks can vary depending on individual factors and the specific type of HRT.
Is HRT suitable for everyone experiencing menopause or andropause?
+No, HRT is not suitable for everyone. It depends on various factors, including your medical history, current health status, and personal preferences. Some individuals may have contraindications or may not experience significant benefits from HRT.
How long does HRT typically last?
+The duration of HRT can vary. Some individuals may require HRT for a few years, while others may need it for a longer period. The length of treatment depends on the specific condition being treated and the individual’s response to therapy.


