What Does Cv Stand For Resume
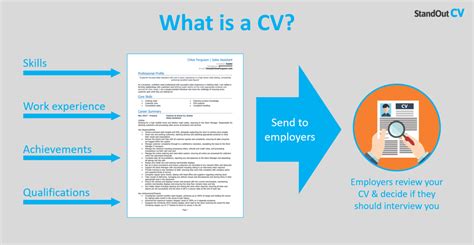
The term CV, short for curriculum vitae, is a comprehensive document used primarily in academic, research, and professional contexts, especially in Europe, Canada, and other regions where it is considered a standard part of the job application process. A CV differs from a resume in terms of length, content, and purpose, offering a more detailed overview of an individual's academic and professional background.
The Comprehensive Curriculum Vitae

A CV, in its truest form, is an in-depth portrayal of an individual’s academic and professional journey. Unlike a resume, which is typically concise and tailored to a specific job role, a CV provides a holistic view of one’s expertise, achievements, and experiences.
Key Components of a CV
The structure of a CV is designed to showcase an individual’s entire career trajectory, including:
- Education: Details of all academic qualifications, from undergraduate degrees to postgraduate certifications.
- Research Experience: A section dedicated to research projects, publications, and contributions to the academic community.
- Professional Experience: An extensive list of work experiences, including roles, responsibilities, and achievements.
- Awards and Honors: Recognition for academic or professional excellence.
- Certifications and Licensures: Validations of specialized skills and knowledge.
- Publications: A list of published works, articles, or books.
- Memberships and Affiliations: Associations with professional bodies or organizations.
The length of a CV can vary significantly, often ranging from two to ten pages, depending on an individual's career stage and the depth of their experiences.
When to Use a CV
CVs are commonly employed in academic settings, such as when applying for graduate programs, research positions, or academic roles. They are also favored in certain industries, particularly in Europe, where they are often the primary document used for job applications.
| CV Focus | Resume Focus |
|---|---|
| Academic Achievements | Specific Job Skills |
| Research Experience | Professional Experiences |
| Publications | Work History |

Resume: The Concise Career Summary

A resume, on the other hand, is a briefer and more focused document tailored to a specific job application. It is designed to capture an employer’s attention and highlight an applicant’s suitability for the role.
Key Elements of a Resume
Resumes typically include:
- Personal Information: Name, contact details, and professional email.
- Professional Summary: A concise paragraph outlining key skills and experiences.
- Work Experience: A list of relevant job roles with descriptions of responsibilities and achievements.
- Education: Details of the highest academic qualification, with an emphasis on how it relates to the job role.
- Skills: A list of technical and soft skills relevant to the job.
Resumes are generally kept to one or two pages, ensuring a quick and efficient read for recruiters.
When to Use a Resume
Resumes are the preferred document for job applications in the United States and many other parts of the world. They are particularly useful when applying for roles in industries that value practical experience and specific skill sets.
Understanding the Differences
While both documents serve the purpose of showcasing an individual’s professional qualifications, they differ in scope and purpose. A CV is a comprehensive record of an individual’s entire career, while a resume is a strategic document designed to highlight specific skills and experiences relevant to a particular job role.
The choice between a CV and a resume often depends on the cultural context, industry norms, and the specific job requirements. In some cases, both may be required, with the CV providing a broader overview and the resume offering a more targeted snapshot of an individual's career.
Tailoring Your Application
Whether you’re crafting a CV or a resume, it’s essential to tailor the document to the specific job or role you’re applying for. This involves highlighting the experiences and skills that are most relevant to the position, ensuring your application stands out to recruiters.
For instance, when applying for a role in a research-intensive industry, a CV might be more appropriate, as it can provide a detailed account of your academic and research achievements. Conversely, for a role in a fast-paced, results-driven industry, a resume might be preferred, as it offers a concise overview of your practical skills and experiences.
What is the difference between a CV and a resume in terms of length and content?
+A CV is a comprehensive document that typically includes all academic qualifications, research experience, professional experience, awards, certifications, publications, and affiliations. It can range from two to ten pages, depending on an individual’s career stage and depth of experience. In contrast, a resume is a briefer, more focused document tailored to a specific job role. It includes personal information, a professional summary, work experience, education, and skills, and is generally kept to one or two pages.
When should I use a CV, and when should I use a resume?
+CVs are commonly used in academic settings, such as when applying for graduate programs, research positions, or academic roles. They are also favored in certain industries, particularly in Europe, where they are often the primary document used for job applications. Resumes, on the other hand, are the preferred document for job applications in the United States and many other parts of the world. They are particularly useful when applying for roles in industries that value practical experience and specific skill sets.
How can I decide between a CV and a resume for my job application?
+The choice between a CV and a resume often depends on cultural context, industry norms, and specific job requirements. If the job listing specifically requests a CV, it’s best to provide one. However, if the listing doesn’t specify, consider the nature of the role and the industry. A CV is often preferred for roles in academia or research-intensive fields, while a resume is typically used for roles in industries that value practical experience and specific skill sets.



