What Is Asset Management

Asset management is a vital component of the financial industry, encompassing a wide range of activities aimed at optimizing the value and performance of various assets. It involves the strategic planning, organization, and control of financial resources to achieve specific investment goals. From individuals seeking to grow their wealth to institutional investors managing vast portfolios, asset management plays a pivotal role in navigating the complex world of investments.
Understanding Asset Management
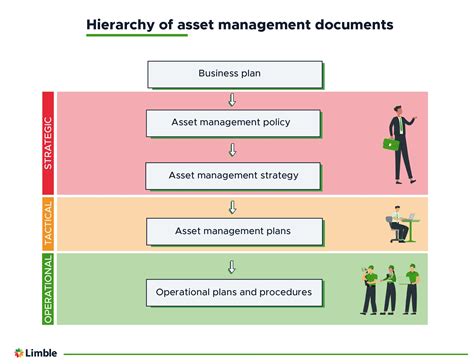
At its core, asset management is about making informed decisions to enhance the value of assets over time. This involves a deep understanding of market dynamics, risk management strategies, and the intricate balance between potential returns and associated risks. Whether it’s managing stocks, bonds, real estate, or alternative investments, the goal remains consistent: to maximize returns while mitigating risks.
Key Components of Asset Management
Asset management encompasses several critical aspects, each playing a unique role in the overall investment strategy.
- Investment Research and Analysis: This involves thorough market research, studying economic trends, and analyzing individual securities or asset classes. Asset managers employ various tools and techniques to identify undervalued assets, assess risk, and make informed investment decisions.
- Portfolio Construction and Management: Asset managers construct and manage portfolios by selecting and allocating assets based on investment objectives, risk tolerance, and market conditions. This process requires a nuanced understanding of asset correlations and diversification strategies.
- Risk Management: Effective risk management is at the heart of asset management. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to protect the portfolio's value. Asset managers employ risk management techniques to ensure the portfolio remains aligned with the client's risk appetite and investment goals.
- Performance Evaluation and Reporting: Regular performance evaluation is crucial to assess the success of investment strategies. Asset managers provide comprehensive reports to clients, detailing the portfolio's performance, risks, and any deviations from the initial investment plan.
The asset management process is highly iterative, with managers continuously monitoring market conditions, adjusting portfolios, and making strategic decisions to maximize returns and manage risks effectively.
Asset Management Strategies

Asset management employs a variety of strategies tailored to different investment objectives and risk profiles. Here’s an overview of some common strategies:
Passive vs. Active Management
Passive management involves investing in assets that track a market index, such as an S&P 500 index fund. This strategy aims to replicate the performance of the market, requiring minimal intervention. On the other hand, active management involves making strategic investment decisions to outperform the market. Active managers analyze individual securities, market trends, and economic factors to identify undervalued assets and capitalize on market inefficiencies.
Growth vs. Value Investing
Growth investing focuses on identifying companies with strong growth potential, often in emerging industries or sectors. These companies may not pay dividends but have the potential for significant capital appreciation. In contrast, value investing seeks to identify undervalued assets, often mature companies with stable earnings. Value investors believe that these companies’ stock prices are temporarily depressed and will eventually rise, providing capital gains.
Alternative Investments
Alternative investments encompass a range of asset classes beyond traditional stocks and bonds. These include real estate, private equity, hedge funds, and commodities. Alternative investments are often used to diversify portfolios and provide access to less correlated asset classes, potentially reducing overall portfolio risk.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation involves determining the optimal mix of asset classes within a portfolio based on the investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals. This strategy aims to balance risk and return by allocating assets across different sectors, industries, and geographic regions.
| Asset Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Equities | Ownership shares in companies, also known as stocks. |
| Fixed Income | Assets that provide a fixed stream of income, such as bonds. |
| Cash and Equivalents | Highly liquid assets, including cash and short-term investments. |
| Real Estate | Physical properties, such as residential or commercial buildings. |
| Commodities | Tangible assets like gold, oil, or agricultural products. |

The Role of Asset Managers
Asset managers are the experts who guide investors through the complex world of investments. They bring a wealth of knowledge, experience, and analytical skills to the table, enabling them to make informed decisions on behalf of their clients. Asset managers are responsible for:
- Conducting thorough research and analysis to identify investment opportunities.
- Constructing and managing portfolios tailored to client needs and objectives.
- Implementing risk management strategies to protect portfolio value.
- Monitoring market conditions and adjusting portfolios as necessary.
- Providing regular performance reports and client communication.
Asset Management and Institutional Investors
Asset management is particularly crucial for institutional investors, such as pension funds, insurance companies, and endowments. These entities manage vast sums of money and have a fiduciary duty to their beneficiaries or shareholders. Asset managers working with institutional investors must navigate unique challenges, including:
- Long-Term Focus: Institutional investors often have long-term investment horizons, requiring asset managers to adopt a strategic, patient approach.
- Risk Management: Given the scale of their investments, institutional investors prioritize risk management to protect the value of their portfolios.
- Regulatory Compliance: Asset managers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards.
- Diversification: Institutional investors often require highly diversified portfolios to spread risk across various asset classes and sectors.
Asset Management in Practice

Asset management is a dynamic and evolving field, constantly adapting to market changes and investor needs. Here’s a real-world example to illustrate its application:
Case Study: Asset Management for Retirement Planning
Imagine a retired couple, John and Jane, who have saved a substantial sum over their working lives and now seek to manage their assets effectively for a comfortable retirement. They engage an asset manager to help them achieve their financial goals.
The asset manager conducts a thorough assessment of John and Jane's financial situation, including their risk tolerance, investment objectives, and time horizon. Based on this assessment, the manager constructs a diversified portfolio tailored to their needs. The portfolio might include a mix of equities for growth, fixed-income securities for regular income, and alternative investments for diversification.
As market conditions change, the asset manager regularly reviews and adjusts the portfolio. They may rebalance the asset allocation to ensure it remains aligned with John and Jane's risk tolerance and investment goals. The manager also provides regular performance reports, helping John and Jane understand how their investments are performing and making informed decisions about their retirement finances.
Future Trends in Asset Management
The asset management industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing investor preferences, and evolving market dynamics. Here are some key trends to watch:
Technology and Automation
Asset managers are increasingly leveraging technology and automation to enhance their investment processes. From algorithmic trading to artificial intelligence-powered research tools, technology is transforming the way asset managers identify investment opportunities and manage portfolios.
Sustainable and Impact Investing
There is a growing focus on sustainable and impact investing, where investors seek to align their financial goals with their values and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations. Asset managers are developing strategies and funds that incorporate ESG factors into investment decisions.
Digital Assets and Cryptocurrencies
The emergence of digital assets and cryptocurrencies has opened up new investment opportunities and challenges. Asset managers are exploring ways to integrate these assets into portfolios, while also navigating the regulatory and technological complexities associated with these emerging asset classes.
Regulation and Transparency
Increasing regulatory scrutiny and investor demand for transparency are shaping the asset management landscape. Asset managers are adapting to stricter regulations and enhancing their reporting and communication practices to meet investor expectations.
How do asset managers generate returns for investors?
+
Asset managers generate returns for investors by employing various strategies, such as active portfolio management, strategic asset allocation, and timely investment decisions. They aim to maximize returns while managing risks effectively, ensuring investors’ financial goals are met.
What are the key benefits of asset management for individual investors?
+
Asset management offers individual investors access to expert guidance, portfolio diversification, and risk management strategies. It helps them navigate complex markets, achieve their financial goals, and maximize returns while managing risks.
How does asset management differ from wealth management?
+
Asset management focuses primarily on managing investments and financial assets, while wealth management takes a more holistic approach, encompassing a range of financial services, including investment management, tax planning, estate planning, and more. Wealth management often involves a broader scope and a deeper relationship with the client.


