What Is Normal Barometric Pressure
Barometric pressure, often referred to as atmospheric pressure, is a fundamental concept in meteorology and physics. It plays a crucial role in understanding weather patterns, altitude measurements, and even our daily experiences. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of normal barometric pressure, exploring its definition, measurements, variations, and significance in various fields.
Understanding Barometric Pressure
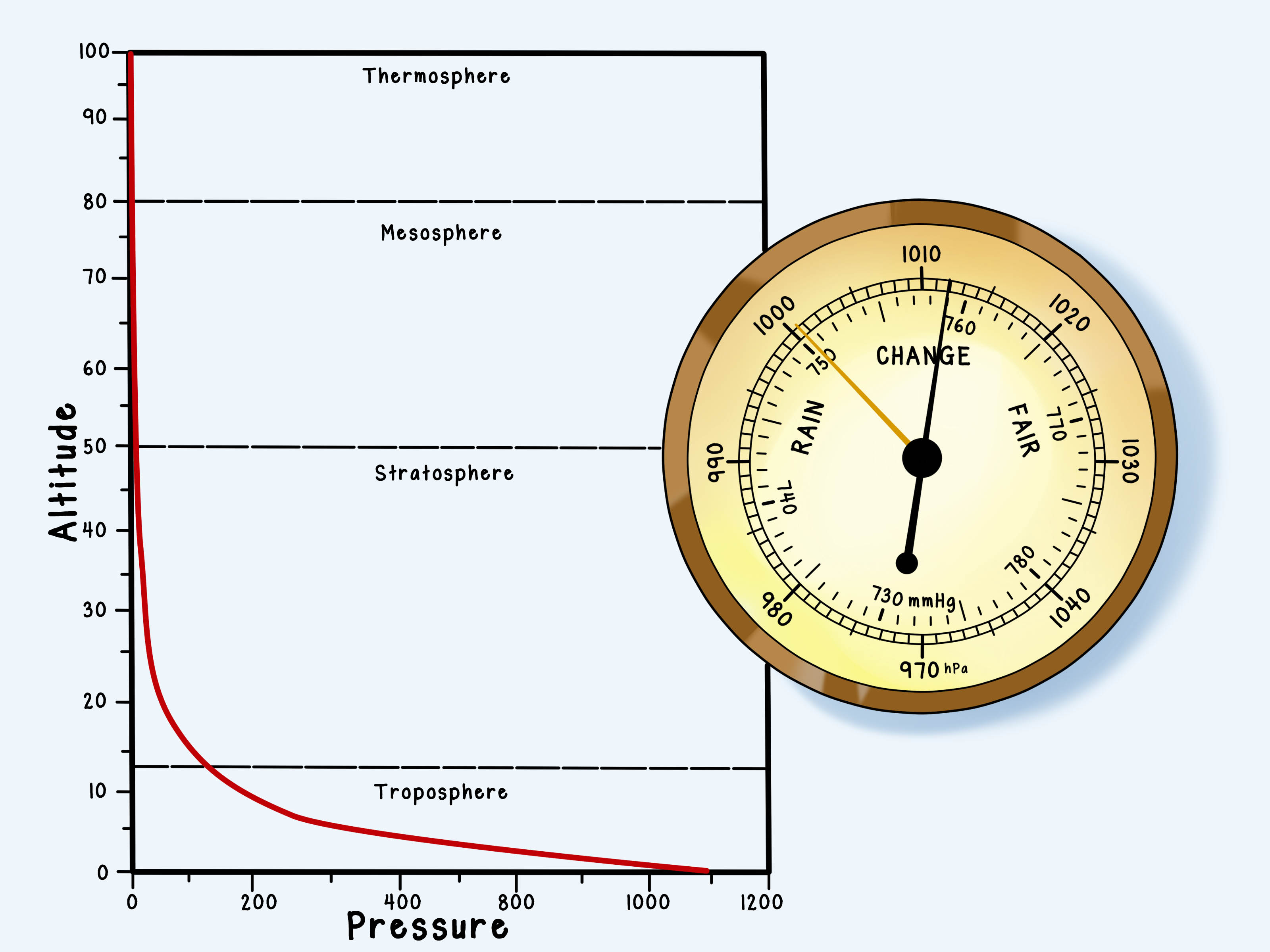
Barometric pressure represents the force exerted by the weight of the atmosphere on a given surface area. It is typically measured in units such as millibars (mb), inches of mercury (inHg), or hectopascals (hPa). The standard unit for atmospheric pressure is the pascal (Pa), but for practical purposes, hectopascals are commonly used.
Normal barometric pressure refers to the average atmospheric pressure at sea level, which serves as a reference point for measurements and calculations. This pressure value is essential for various scientific and practical applications, including weather forecasting, aviation, and even medical diagnostics.
Standard Atmospheric Pressure

The standard atmospheric pressure is defined as 1013.25 hPa (or 101.325 kPa) at sea level. This value is based on international agreements and is used as a baseline for atmospheric pressure measurements worldwide. However, it’s important to note that actual atmospheric pressure can vary depending on geographical location, altitude, and weather conditions.
For instance, locations at higher altitudes, such as mountain ranges, experience lower barometric pressures due to the reduced weight of the atmosphere above. Conversely, areas closer to sea level, like coastal regions, generally have higher atmospheric pressures.
Altitude and Barometric Pressure
Altitude has a significant impact on barometric pressure. As one ascends to higher altitudes, the air pressure decreases because there are fewer air molecules above to exert force. This phenomenon is crucial for understanding altitude-related physiological effects, such as those experienced by mountain climbers or pilots.
| Altitude (ft) | Barometric Pressure (hPa) |
|---|---|
| Sea Level | 1013.25 |
| 5000 ft | 867.78 |
| 10,000 ft | 740.58 |
| 15,000 ft | 598.95 |

Weather and Barometric Pressure
Barometric pressure is intimately linked to weather patterns and forecasts. Changes in atmospheric pressure can indicate the approach of storms, fronts, or other significant weather events. A falling barometric pressure often suggests an impending storm, while rising pressure may indicate improving weather conditions.
Barometric Pressure and Storms
During storms, such as hurricanes or typhoons, barometric pressure drops significantly. This drop in pressure is a key indicator for meteorologists and weather enthusiasts, allowing them to track and predict the intensity and movement of these powerful weather systems.
Barometric Pressure Measurement Tools
Various instruments are used to measure barometric pressure, including barometers, aneroid barometers, and electronic pressure sensors. These devices provide precise readings, aiding in weather monitoring and forecasting.
Applications of Barometric Pressure
The understanding and measurement of barometric pressure have numerous practical applications across different fields:
- Aviation: Pilots rely on accurate barometric pressure readings for altitude determination, navigation, and safety during flights.
- Meteorology: Meteorologists use barometric pressure data to create weather models, forecast storms, and analyze atmospheric patterns.
- Medicine: Changes in barometric pressure can impact physiological functions, and medical professionals consider it when treating patients with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions.
- Environmental Science: Researchers study barometric pressure variations to understand climate change, pollution dispersion, and ecosystem dynamics.
- Engineering: Engineers consider barometric pressure in designing structures, especially those at high altitudes or underwater, to ensure stability and safety.
Barometric Pressure and Health
Barometric pressure fluctuations can have subtle effects on human health. Some individuals with chronic conditions, such as joint pain or migraines, may experience symptom exacerbation during rapid pressure changes. Additionally, altitude-related illnesses like acute mountain sickness are associated with rapid ascents and subsequent changes in barometric pressure.
Future Implications

As our understanding of atmospheric dynamics advances, the role of barometric pressure in various fields becomes increasingly important. The integration of advanced pressure sensors and data analytics allows for more accurate weather predictions and climate modeling. Additionally, the study of barometric pressure variations can provide insights into long-term climate trends and the impact of human activities on the atmosphere.
The Role of Technology
Technological advancements, such as the development of compact, accurate pressure sensors and real-time data transmission, have revolutionized barometric pressure measurements. These innovations enable more precise weather forecasting, especially in remote or mountainous regions.
How does barometric pressure affect daily life?
+Barometric pressure variations can impact our daily experiences. For example, changes in pressure can affect the performance of electronic devices, especially those with sensitive components. Additionally, some individuals may experience mild discomfort or changes in their physical well-being during significant pressure shifts.
Can barometric pressure affect indoor environments?
+Yes, barometric pressure can influence indoor air quality and pressure differentials between the interior and exterior of buildings. This is particularly relevant for buildings with advanced HVAC systems or those designed to maintain specific environmental conditions.
What is the significance of barometric pressure in climate science?
+Barometric pressure data is crucial for climate science as it provides insights into atmospheric circulation, weather patterns, and long-term climate trends. By analyzing historical and current pressure data, scientists can better understand the Earth’s climate system and make predictions about future changes.