Where Is Gaza Located
The Gaza Strip, or simply Gaza, is a small yet significant geographical entity nestled in the Middle East. It holds immense historical, political, and cultural importance, making its geographical location a crucial topic of discussion. Understanding where Gaza is located provides context for its role in regional affairs and its impact on global geopolitics.
Geographical Overview of Gaza

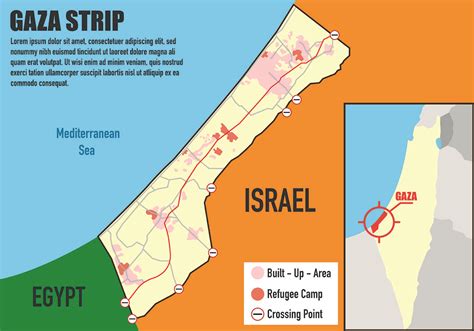
Gaza is a narrow coastal territory situated on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It forms a part of the Levant region, a historical area encompassing parts of modern-day Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, and the Palestinian territories.
Bordered by Israel to the north and east and by Egypt to the southwest, Gaza is approximately 41 kilometers (25 miles) long and 6 to 12 kilometers (4 to 7.5 miles) wide. The territory has a total area of about 360 square kilometers (140 square miles), making it one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
Topographical Features
Gaza’s landscape is primarily characterized by its coastal plain, which extends along the Mediterranean Sea. The territory has a flat topography with a gradual elevation towards the south. The northern part of Gaza is slightly more elevated, with a few small hills and ridges, while the southern region is predominantly flat and fertile.
The Gaza Strip is also home to the Gaza City, the largest urban center and the economic hub of the territory. Gaza City is located on the coast and serves as the administrative capital of the Gaza Governorate.
| Topographical Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Coastal Plain | A flat, low-lying region along the Mediterranean Sea, characterized by sandy beaches and fertile agricultural lands. |
| Northern Hills | A series of small hills and ridges in the northern part of Gaza, providing a slightly elevated landscape. |
| Southern Plains | Flat and fertile lands in the southern region of Gaza, known for their agricultural productivity. |

Geopolitical Significance
Gaza’s geographical location has contributed to its strategic importance in the region. It serves as a key access point to the Mediterranean Sea, offering a potential maritime trade route for neighboring countries. Additionally, its proximity to major cities like Jerusalem, Tel Aviv, and Cairo has made it a focal point in regional conflicts and negotiations.
Historical and Cultural Context

The history of Gaza stretches back thousands of years, making it a region of immense cultural and archaeological significance. Ancient Gaza was a major city and a strategic trading post, connecting the Mediterranean world with the Arabian Peninsula and Africa. It has been influenced by various civilizations, including the Philistines, Egyptians, Persians, Greeks, Romans, and Arabs.
Cultural Diversity
Gaza’s diverse cultural heritage is reflected in its architecture, cuisine, and traditions. The territory is home to a rich mix of Arab, Islamic, and Palestinian influences, with a strong sense of community and cultural pride. Traditional Palestinian crafts, such as embroidery and pottery, thrive in Gaza, showcasing its unique artistic heritage.
Religious Significance
Gaza holds religious significance for multiple faiths. It is mentioned in the Bible and is associated with biblical figures like Samson and Delilah. In Islamic tradition, Gaza is linked to several key figures, including the Prophet Muhammad’s companion, Ubada ibn as-Samit, who is believed to have been buried in the city.
Modern Challenges and Opportunities
Today, Gaza faces numerous challenges due to its complex political situation. The territory is under the control of Hamas, a Palestinian political party and militant group, which has led to international sanctions and restricted access to resources. Despite these challenges, Gaza’s resilient population continues to strive for economic growth, cultural preservation, and political stability.
The Gaza Strip has a strong entrepreneurial spirit, with innovative businesses emerging in various sectors. The territory's youth, despite facing significant obstacles, are driving social and economic change, utilizing technology and creativity to build a better future.
International Support and Aid
Gaza receives significant international aid and support from various organizations and countries. This aid focuses on providing humanitarian assistance, supporting healthcare and education, and promoting economic development. International efforts aim to improve the living conditions of Gaza’s residents and foster a path towards peace and prosperity.
What is the population of Gaza?
+The population of the Gaza Strip is estimated to be around 2.1 million people, making it one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
How does Gaza’s geographical location impact its economy?
+Gaza’s coastal location provides opportunities for maritime trade and fishing, contributing to its economy. However, limited access to resources and international sanctions have hindered its economic growth.
What are the main industries in Gaza?
+Gaza’s main industries include agriculture, fishing, and manufacturing. The territory also has a growing entrepreneurial sector, with businesses in technology, handicrafts, and services.
How has Gaza’s cultural heritage been preserved despite challenges?
+Gaza’s cultural heritage is preserved through traditional arts, cuisine, and community events. Local initiatives and international support also play a crucial role in safeguarding its cultural identity.



