What Does It Mean To Ovulate
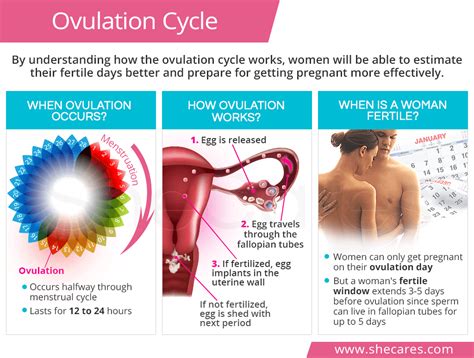
Ovulation is a fundamental process in the female reproductive system, marking a crucial phase in the menstrual cycle. It is a complex event that holds significant importance for both fertility and overall health. Understanding ovulation is key to managing reproductive health and planning for pregnancy or contraception.
The Science Behind Ovulation
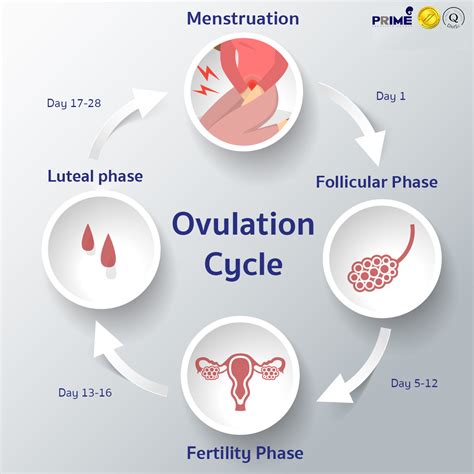
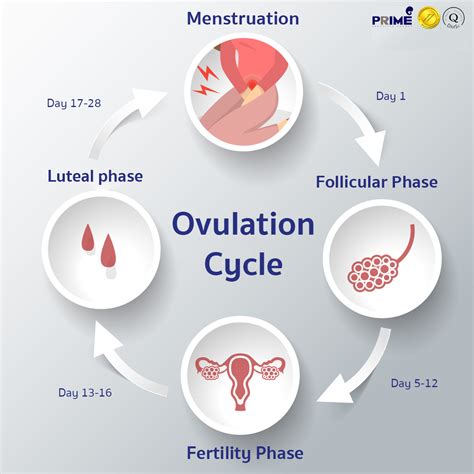
Ovulation is the release of a mature egg, or ovum, from an ovarian follicle. This process is regulated by a delicate interplay of hormones, including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones prompt the development and release of an egg from one of the ovaries, typically on a monthly basis.
The journey of ovulation begins during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. FSH stimulates the growth of multiple follicles within the ovaries, each containing an immature egg. Over time, one dominant follicle emerges, continuing to mature under the influence of FSH and estrogen. As this follicle matures, it produces increasing amounts of estrogen, which thickens the uterine lining (endometrium) in preparation for a potential pregnancy.
The surge in LH marks the onset of ovulation. This surge triggers the release of the mature egg from the ovarian follicle, propelling it into the fallopian tube. Here, the egg awaits fertilization by sperm. If fertilization occurs, the resulting embryo travels down the fallopian tube to implant in the prepared uterine lining, initiating pregnancy. If fertilization doesn't occur, the egg dissolves, and hormone levels drop, signaling the start of the menstrual period.
Ovulation and Fertility
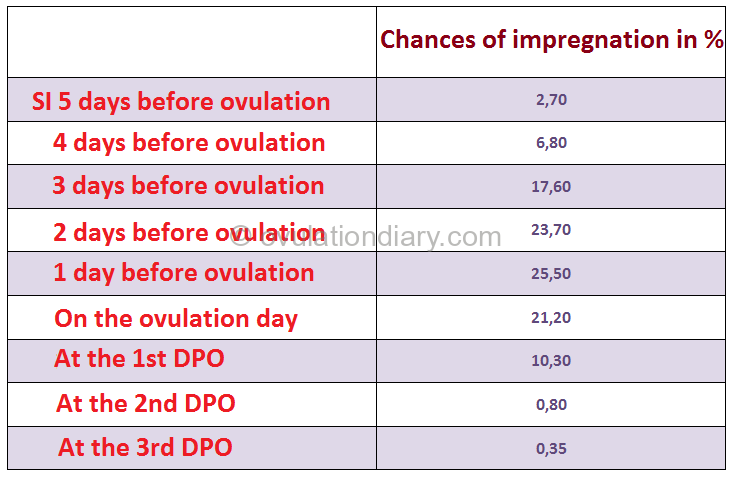
Ovulation is the key to fertility, as it is the window of opportunity for sperm to fertilize the egg. Understanding this process is vital for those trying to conceive. By tracking ovulation, individuals can identify their most fertile days and optimize their chances of pregnancy.
Several methods exist to track ovulation, including monitoring basal body temperature, using ovulation predictor kits, and observing cervical mucus changes. These methods can help individuals pinpoint the days when they are most likely to conceive.
| Ovulation Tracking Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Basal Body Temperature | Tracking daily body temperature to detect the slight rise that occurs after ovulation. |
| Ovulation Predictor Kits | Detecting the surge in LH hormones through urine tests. |
| Cervical Mucus Observation | Noticing changes in cervical mucus, which becomes thinner and more abundant around ovulation. |
For those looking to avoid pregnancy, understanding ovulation is also crucial. By avoiding intercourse during the fertile window, individuals can reduce the risk of unintended pregnancy. However, it's important to note that ovulation can be unpredictable, and additional contraceptive methods are often necessary for reliable pregnancy prevention.
Health Implications of Ovulation
Ovulation isn’t just about fertility; it also has broader health implications. The hormones involved in ovulation can influence overall health and well-being. For instance, the menstrual cycle, driven by ovulation, can impact mood, energy levels, and even certain health conditions.
Women with irregular ovulation or anovulation (absence of ovulation) may experience hormonal imbalances, leading to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or irregular periods. These conditions can affect fertility and overall health, highlighting the importance of regular ovulation for optimal well-being.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Ovulation
Lifestyle factors can significantly influence ovulation. Stress, for example, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance, impacting ovulation and fertility. Similarly, weight and diet play crucial roles. Both underweight and overweight individuals may experience ovulatory dysfunction, emphasizing the importance of a healthy lifestyle for optimal reproductive health.
Nutrition and Ovulation
Nutrition is a key factor in ovulation. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals supports hormonal balance and ovulation. Certain nutrients, like vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, have been linked to improved fertility and ovulatory function.
On the other hand, excessive intake of certain substances, such as caffeine and alcohol, can disrupt ovulation and reduce fertility. It's essential to maintain a healthy, balanced diet to support optimal ovulation and overall reproductive health.
Future Perspectives
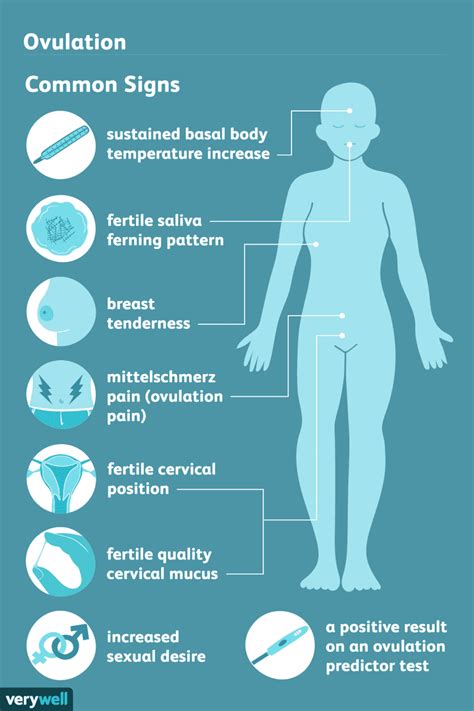
Ongoing research continues to deepen our understanding of ovulation and its implications. Advances in fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), offer hope for those struggling with ovulatory disorders or infertility. Additionally, emerging technologies, such as ovulation tracking apps and at-home fertility tests, provide new tools for individuals to monitor their reproductive health.
As our knowledge of ovulation and its role in fertility and health expands, so do the opportunities for improved reproductive health management and personalized fertility solutions.
How long does ovulation last?
+Ovulation typically lasts for a brief period, often less than 24 hours. Once the egg is released, it can survive for around 12 to 24 hours, awaiting fertilization. It’s important to note that the fertile window extends beyond ovulation, as sperm can survive in the reproductive tract for several days.
Can stress affect ovulation?
+Yes, stress can significantly impact ovulation. Chronic stress can disrupt the hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods and ovulation. Managing stress through lifestyle changes and stress-reduction techniques can help regulate ovulation and improve overall reproductive health.
What are some signs of ovulation?
+Some common signs of ovulation include a change in cervical mucus (becoming thinner and more slippery), a slight rise in basal body temperature, and breast tenderness. Additionally, some women may experience mild abdominal pain or cramping, known as mittelschmerz, during ovulation.