What Is The Difference Between Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are two powerful and transformative technologies that have revolutionized numerous industries and our daily lives. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the difference between AI and ML is crucial for professionals, enthusiasts, and anyone interested in harnessing the potential of these technologies. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of AI and ML, exploring their definitions, historical backgrounds, and practical applications.
Unraveling the Concepts: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence is a branch of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI encompasses a wide range of technologies and techniques, including natural language processing, computer vision, expert systems, and more. The primary goal of AI is to develop systems that can perceive, reason, learn, and make decisions akin to human cognitive abilities.
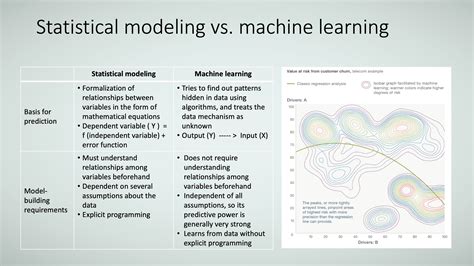
Machine Learning, on the other hand, is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time. ML algorithms use historical data to identify patterns, make predictions, and automate decision-making processes without being explicitly programmed. This self-learning capability is what sets ML apart from traditional programming approaches.
Historical Perspective and Evolution

The origins of Artificial Intelligence can be traced back to the 1950s, when researchers and computer scientists began exploring the concept of creating machines that could simulate human intelligence. Early AI research focused on developing rule-based systems and symbolic reasoning, laying the foundation for expert systems and knowledge-based approaches. The 1980s and 1990s saw significant advancements in AI, with the development of neural networks and expert systems gaining traction.
Machine Learning emerged as a distinct field in the 1990s, building upon the concepts and techniques of AI. Researchers recognized the potential of ML to address complex problems by leveraging large datasets and statistical analysis. The development of powerful computing resources and the availability of vast amounts of data fueled the growth of ML, leading to breakthroughs in areas such as image recognition, natural language understanding, and predictive analytics.
Key Differences and Applications
Artificial Intelligence encompasses a broader range of technologies and methodologies, aiming to replicate human-like intelligence in machines. AI systems can perform a wide array of tasks, from simple rule-based decision-making to complex problem-solving and pattern recognition. Some common applications of AI include virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, recommendation engines, and intelligent automation in various industries.
Machine Learning, as a subset of AI, focuses specifically on the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn from data. ML algorithms can be broadly categorized into supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training models using labeled data, while unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data to identify patterns and relationships. Reinforcement learning, inspired by behavioral psychology, trains agents to make sequential decisions in dynamic environments.
Practical Examples and Use Cases
Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized industries such as healthcare, finance, and customer service. In healthcare, AI-powered systems can analyze medical images, assist in diagnosis, and provide personalized treatment recommendations. AI-based chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer support, offering 24⁄7 assistance and personalized interactions. In finance, AI algorithms detect fraud, optimize investment strategies, and automate financial processes.
Machine Learning finds extensive applications in data-intensive domains. ML algorithms power recommendation engines in e-commerce and streaming platforms, offering personalized product suggestions and content recommendations. In finance, ML models analyze market trends, predict stock prices, and detect anomalies in transaction data. ML is also instrumental in image and speech recognition, enabling technologies like facial recognition, voice assistants, and autonomous vehicles.
| Category | Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad range of technologies and methodologies | Subset of AI focused on data-driven learning |
| Learning Approach | Rule-based, symbolic reasoning, and knowledge-based | Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning |
| Data Requirements | Can work with structured and unstructured data | Relies on large volumes of labeled or unlabeled data |
| Applications | Virtual assistants, autonomous systems, recommendation engines | Image recognition, natural language processing, predictive analytics |

The Future of AI and ML: Synergy and Innovations
The future of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning is promising, with ongoing research and advancements pushing the boundaries of what is possible. As AI systems become more sophisticated, they are expected to play a pivotal role in solving complex global challenges, from climate change to healthcare accessibility. The integration of AI and ML with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing, will unlock new opportunities and drive innovation across industries.
Furthermore, the ethical considerations surrounding AI and ML are gaining prominence. Ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems is crucial to building trust and mitigating potential biases. Researchers and developers are actively working on developing responsible AI practices, addressing privacy concerns, and promoting inclusive and beneficial AI solutions.
Potential Innovations and Advancements
In the coming years, we can anticipate significant advancements in AI and ML, including:
- Enhanced Natural Language Understanding: AI systems will continue to improve their ability to comprehend and generate human-like language, enabling more sophisticated conversational agents and language-based interfaces.
- Advanced Computer Vision: ML algorithms will become more accurate and efficient in image and video analysis, leading to breakthroughs in areas such as autonomous driving, medical imaging, and surveillance systems.
- Predictive Analytics and Decision Support: AI-powered predictive models will become more sophisticated, aiding businesses in forecasting trends, optimizing operations, and making data-driven decisions.
- AI-as-a-Service: The rise of AI-as-a-Service platforms will make AI technologies more accessible and affordable, empowering businesses of all sizes to leverage AI capabilities without extensive infrastructure investments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are some real-world examples of Artificial Intelligence in use today?
+AI is pervasive in our daily lives. Some real-world examples include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, self-driving cars, fraud detection systems in banking, personalized product recommendations on e-commerce platforms, and medical diagnosis support systems.
How does Machine Learning differ from traditional programming approaches?
+Traditional programming involves explicit instruction-based coding, where developers provide step-by-step rules for a computer to follow. In contrast, Machine Learning algorithms learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each scenario.
What are some challenges and ethical considerations in the development and deployment of AI systems?
+Challenges include ensuring data quality and privacy, addressing biases in training data, and developing transparent and explainable AI systems. Ethical considerations involve responsible AI development, mitigating potential harm, and ensuring equitable access to AI technologies.
How can businesses leverage AI and ML to gain a competitive advantage?
+Businesses can utilize AI and ML to enhance customer experiences, optimize operations, and gain insights from data. AI-powered analytics can identify trends, improve decision-making, and drive innovation, giving businesses a competitive edge.



